Management assertions in auditing
- Home
- Management assertions in auditing


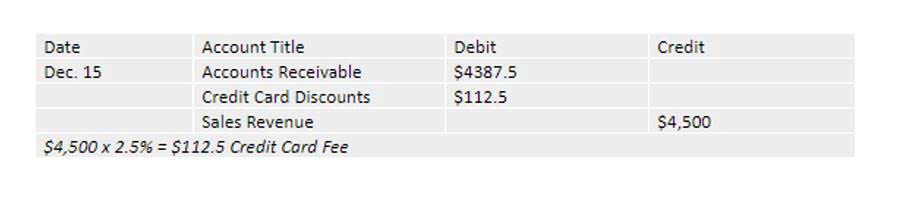
The accuracy assertion means the amounts of recorded transactions are accurate. The related Unrealized Holding Gain or Loss – Income account that is debited and credited throughout the year audit management assertions can easily contain errors. All disclosures that should have been included in the financial statements have been included. All transactions that were supposed to be recorded have been recognized in the financial statements. Transactions recognized in the financial statements have occurred and relate to the entity. The auditor’s approach to gathering evidence is not static; it is responsive to the findings as the audit progresses.
In other words, it helps ensure companies record transactions that were supposed to have been recognized. For account balances, it checks the completeness of asset, liability, and equity balances. Therefore, other names may include management or financial statement assertions.
Presentation and disclosure assertion refers to the proper classification, description, and disclosure of information in the financial statements. Auditors review whether the financial statements comply with relevant accounting frameworks, ensuring that they provide users with a clear and accurate understanding of the company’s financial position and performance. Assets, liabilities, and equity interests are included in the financial statements at appropriate amounts, and any resulting valuation or allocation adjustments are appropriately recorded.
This assertion is very closely related to the occurrence assertion for transactions. For example, an auditor may want to examine payroll records to make sure that all salaries and wages expenses have been recorded in the proper period. This may include an examination of payroll records, a payroll journal, an active employee list, and any payroll accruals that were made and reversed in the period being examined.

At the end of this article, you can also see the summary of all assertions and their usages. For example, liabilities on the balance sheet should be separated into current and long-term debt. And the related disclosures for long-term debt should be understandable and include relevant details such as maturity dates, payment schedules, and interest rates. Classification – that transactions are recorded in the appropriate accounts – for example, the purchase of raw materials has not been posted to repairs and maintenance. This assertion concerns the definition of “assets” in the contextual framework.

He began his career with Ernst & Young in 2003 where he developed his audit expertise over a number of years. Isaac specializes in and has conducted numerous SOC 1 and SOC 2 examinations for a variety of companies—from startups to Fortune 100 companies. Isaac enjoys helping his clients understand and simplify their compliance activities. He is attentive to his clients’ needs and works meticulously to ensure that each examination and report meets professional standards.

By gaining this understanding, auditors can identify the types of potential misstatements and the https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc factors that may affect the risk of their occurrence. This knowledge informs the design and implementation of audit procedures tailored to the entity’s context. Relevant tests – auditors often use disclosure checklists to ensure that financial statement presentation complies with accounting standards and relevant legislation. Similarly, they help auditors assess if financial statements present a true and fair view. Auditors use audit assertions as guides to help guide their audit process. Usually, they examine each assertion to ensure their conclusions are accurate.
Therefore, this https://www.bookstime.com/ holds tantamount importance from the point of view of not only the auditor but also from the general users of financial statements. Occurrence is an audit assertion that relates to transactions and events. This assertion requires auditors to ensure the transactions recorded in the income statement have actually occurred. The occurrence assertion means that the recorded transactions actually occurred and apply to the company that is being audited.
The occurrence assertion is used to determine whether the transactions recorded on financial statements have taken place. This can range from verifying that a bank deposit has been completed to authenticating accounts receivable balances by determining whether a sale took place on the day specified. When financial statements are prepared, the preparer is asserting the fundamental accuracy of those statements.